Blog Details
Apr-2018
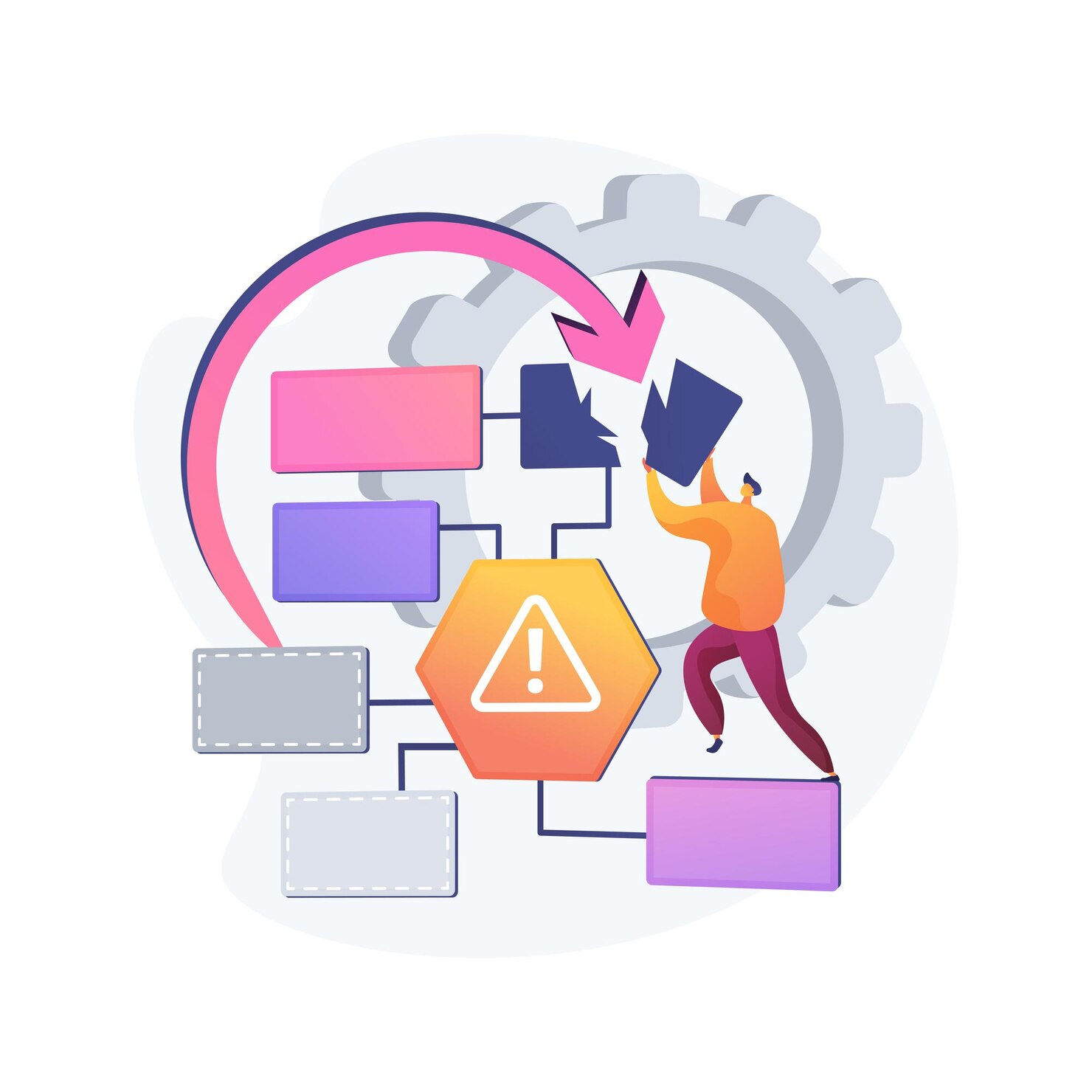
Introduction To Risk Management for Enterprises
Many internal and external factors that can threaten the survival of an enterprise exist. From cyberattacks to regulatory changes to the even more recent global pandemics such as Covid-19, the business world faces many risks. The worst part is that many businesses are usually caught off-guard when such events occur. Perhaps the low probability of these events is why so many enterprises are not proactive in putting in place the necessary measures that help them respond accordingly.
Effective risk management entails anticipating and curbing the impact of the events mentioned above and threats in the business environment. If a business does this successfully, it will survive long term.
Effective risk management requires enterprises to study factors such as:
- Risk source
This refers to an element that can give rise to risk. Risk sources include weather conditions and government agencies.
- Risk event
Risk event refers to the potential occurrence of a particular event that can cause certain outcomes. Risk events may include mass resignations and cyberattacks.
- Risk consequence
A risk consequence refers to the outcome of a risk event. An example of a risk consequence is penalties from a regulator.
- Risk likelihood
Risk likelihood refers to the chance that a risk event will occur, and it may either be low probability or high probability.
Characteristics Of an Effective Risk Management Practice
- It addresses uncertainty effectively.
- An effective risk management practice is incorporated into all the processes in an organization.
- A functional risk management practice is usually structured and systematic.
- An effective risk management practice considers all the information available to an enterprise.
- It is highly responsive to change.
- An effective risk management practice is transparent and very inclusive.
- Its end goal is always to improve the organization.
The Necessary Steps for Effective Risk Management
To effectively hack the risk management process, an enterprise should follow the steps below!
- Identify
The first step is for a firm to identify its strategic position and its risks. This is crucial in helping the firm determine its capacity to deal with whatever risks when they occur. Here, a firm also places itself in a good position to establish its risk tolerance.
- Assess or measure
Once a firm has effectively identified the risks it may face, it then determines the likelihood of occurring and what outcome the risk events will cause. Here, risks are ranked in order of priority, and those with a higher likelihood of occurring and having higher consequences are prioritized.
- Plan
The planning process entails evaluating which measure presents the best risk response action. The main objective of planning here is to minimize the existing threats and maximize the opportunities that present themselves. Some of the best actions to take when responding to existing risks include:
- Avoid
This entails steering clear of the uncertainty by desisting to proceed with a particular course of action. For example, you can avoid going out because the weather looks like it will most likely rain.
- Reduce
This entails taking a course of action that seeks to minimize the chance that an undesired consequence will occur. It simply revolves around taking the most appropriate mitigation controls.
- Transfer
It implies that you identify the third party and pass on the whole of the existing risk to them on behalf of your firm. A good example is passing on risk to insurance companies.
- Share
This implies that you identify the third party and pass on the existing risk to them on behalf of your firm. Sharing risk is a common feature of transactions between customers, suppliers, and even business partners.
- Accept
This course of action entails "settling for the situation" and living with the uncertainty without taking any action.
- Implement
Implementing the responses needed to address risk events entails putting them into action, closely observing their efficacy, and making improvements where needed.
- Communicate
Communicating entails conveying risk information and details of how it is handled to related stakeholders.
Who Are the People Involved In The Risk Management Process?
Some people are crucial to the success of the risk management process. These include:
- Risk Committee
It is a board in charge of oversight and approval of the overall enterprise risk management framework. Some of its roles include providing the resources needed for risk mitigation and evaluating the performance of the implemented risk mitigation.
- Risk Manager
A risk manager is in charge of coordinating the implementation of the enterprise risk management processes. The risk manager also guides the rest of the organization in identifying, assessing, mitigating, and monitoring risks.
- Risk Officer
A risk officer handles the basic risk management activities and maintains documentation of these activities.
- Risk Owner
A risk owner is in charge of managing, monitoring, and controlling risk assigned to them and dealing with threats to maximize existing opportunities.
- Risk Actionee
A risk actionee is in charge of implementing selected risk responses, for example, the risk owner.
Final Take Away
Every organization should be proactive in putting in place measures that mitigate risk events, and it will help them survive all the uncertainties that can affect them in the future.